
Patients may experience the return of memories as nightmares or flashbacks.

Dissociative disorders are often associated with other psychiatric symptoms and conditions, including anxiety, depression, somatic symptom disorders, and eating disorders.
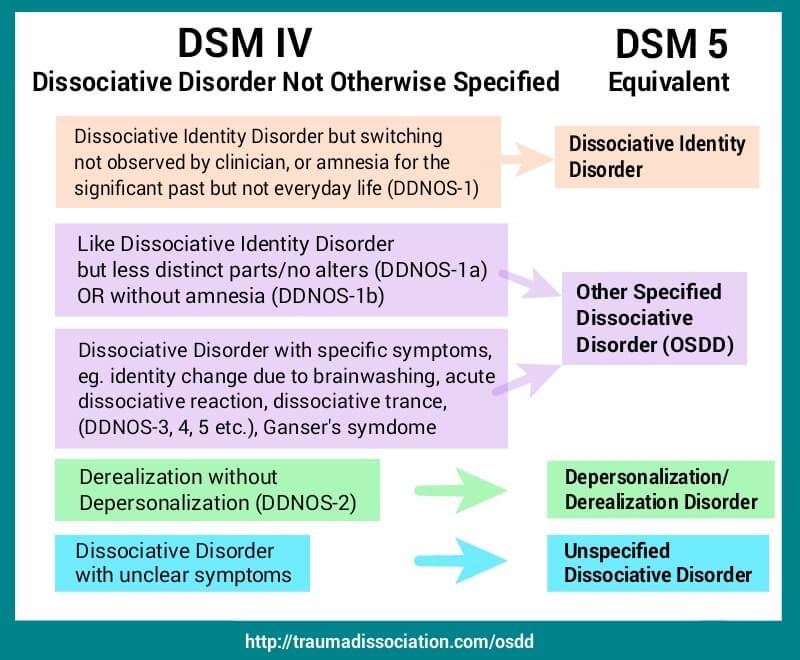
Patients usually experience positive dissociative symptoms such as derealization, fragmentation of identity, and depersonalization (i.e., intrusive and involuntary changes in awareness and behavior) and/or negative dissociative symptoms, such as amnesia or difficulties controlling mental functions. DSM-5 recognizes the following types: dissociative identity disorder, dissociative amnesia (with or without dissociative fugue), depersonalization disorder, as well as other specified dissociative disorder and unspecified dissociative disorder. The disorders are typically seen in individuals with a history of very stressful or traumatic events and often manifest already in childhood. Abnormalities may also be seen in behavior, control of motor functions, and body representation. Dissociative disorders are psychiatric conditions characterized by disruption and/or discontinuity of normal consciousness, memory, identity, and perception.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
